Reinforcement Learning
Paper in NeurIPS 2022 on “VER: Scaling On-Policy RL Leads to the Emergence of Navigation in Embodied Rearrangement”
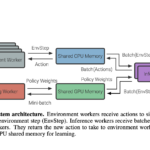
We present Variable Experience Rollout (VER), a technique for efficiently scaling batched on-policy reinforcement learning in heterogenous environments (where different environments take vastly different times to generate rollouts) to many GPUs residing on, potentially, many machines. VER combines the strengths of and blurs the line between synchronous and asynchronous on-policy RL methods (SyncOnRL and AsyncOnRL, respectively). Specifically, it learns from on-policy experience (like SyncOnRL) and has no synchronization points (like AsyncOnRL) enabling high throughput.
Paper in ICRA 2022 on “Graph-based Cluttered Scene Generation and Interactive Exploration using Deep Reinforcement Learning”
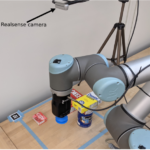
We introduce a novel method to teach a robotic agent to interactively explore cluttered yet structured scenes, such as kitchen pantries and grocery shelves, by leveraging the physical plausibility of the scene. We propose a novel learning framework to train an effective scene exploration policy to discover hidden objects with minimal interactions. First, we define a novel scene grammar to represent structured clutter. Then we train a Graph Neural Network (GNN) based Scene Generation agent using deep reinforcement learning (deep RL), to manipulate this Scene Grammar to create a diverse set of stable scenes, each containing multiple hidden objects. Given such cluttered scenes, we then train a Scene Exploration agent, using deep RL, to uncover hidden objects by interactively rearranging the scene. We show that our learned agents hide and discover significantly more objects than the baselines. We present quantitative results that prove the generalization capabilities of our agents. We also demonstrate sim-to-real transfer by successfully deploying the learned policy on a real UR10 robot to explore real-world cluttered scenes.